In today's distributed workplace, simply managing projects is not enough. Teams need to master the art of remote collaboration to stay competitive and drive results. Traditional project management best practices often fall short when team members are spread across different time zones and rely entirely on digital tools to connect. The old rules no longer guarantee success; a new, more deliberate approach is required to keep projects on track and teams aligned.
This shift demands more than just adopting new software. It requires a fundamental rethinking of how we plan, communicate, and execute. Without the structure of a shared physical office, ambiguity can quickly derail progress, leading to missed deadlines, budget overruns, and disengaged teams. Mastering a modern framework for project management is therefore non-negotiable for any organization that relies on remote or hybrid talent.
This guide provides a comprehensive breakdown of 10 essential project management best practices tailored specifically for the challenges and opportunities of remote work. We will move beyond generic advice to provide actionable strategies you can implement immediately.
You will learn how to:
- Define a crystal-clear project charter and scope to prevent ambiguity.
- Implement effective communication and risk management protocols for distributed teams.
- Adopt agile methodologies that foster flexibility and continuous improvement.
- Master stakeholder engagement, resource allocation, and performance monitoring in a virtual setting.
By applying these targeted strategies, you will be equipped to navigate complexity, boost productivity, and lead your projects to successful completion, ensuring your team not only delivers on time but thrives in a remote-first environment.
1. Clear Project Charter and Scope Definition
One of the most foundational project management best practices is establishing a clear project charter and defining a precise scope from the very beginning. A project charter is a formal document authorizing the project, outlining its objectives, stakeholders, constraints, and success criteria. It acts as a North Star, ensuring everyone involved shares a unified understanding of what needs to be achieved and why.

Without this clarity, projects often suffer from "scope creep," where new requirements are added without a formal process, leading to missed deadlines and budget overruns. This practice, popularized by organizations like the Project Management Institute (PMI) and frameworks such as PRINCE2, prevents ambiguity and aligns expectations across the entire team, including remote and distributed members.
How to Implement This Practice
Creating a robust project charter involves more than just writing down a goal. It requires a collaborative effort to build a comprehensive, yet concise, reference document.
- Involve Key Stakeholders: Bring together sponsors, key team members, and end-users to contribute to the charter. This collaborative approach builds early buy-in and ensures all perspectives are considered.
- Define Key Elements: Your charter should clearly state the project's purpose, quantifiable objectives, defined scope (what is in and what is out), key deliverables, high-level risks, and a list of stakeholders.
- Keep It Accessible: A charter is a living document, not a forgotten file. Store it in a central, accessible location like a shared drive or a project management tool. Ensuring this document is well-maintained is crucial, and exploring documentation best practices can provide a solid framework for keeping all project-related information organized and accessible.
- Review and Revise: Revisit the charter at key project milestones. This allows the team to confirm alignment and make formal adjustments if strategic priorities shift.
By dedicating time to this initial step, you create a stable foundation that supports all future project activities, from resource allocation to task execution, making it an indispensable part of successful project management.
2. Effective Communication Management
Effective communication is the lifeblood of any successful project, and a systematic approach to managing it is one of the most critical project management best practices. This involves creating a plan for how, when, and what information will be shared among stakeholders. A solid communication strategy ensures that every team member, from the project sponsor to the developer, receives the right message at the right time through the right channel.

Without a formal plan, communication becomes chaotic, leading to misunderstandings, duplicated work, and disengaged teams, especially in remote or hybrid environments. Methodologies like Agile and Scrum champion structured communication through daily stand-ups, while companies like GitLab have built their entire remote-first culture on transparent and asynchronous communication protocols. The goal is to make information exchange intentional, not an afterthought.
How to Implement This Practice
Putting an effective communication plan into action requires more than just scheduling meetings. It’s about building a predictable and reliable flow of information that supports the project’s goals.
- Create a Communication Plan: Early in the project, document who needs what information, when they need it, and the best format to deliver it. This plan should define communication types, such as status updates, risk alerts, and decision logs.
- Establish a Regular Rhythm: Implement consistent communication cadences, like daily check-ins for quick updates, weekly tactical meetings for progress reviews, and monthly steering committee meetings for high-level alignment.
- Use the Right Tools for the Job: Differentiate between communication channels. Use instant messaging tools like Slack or Microsoft Teams for urgent, informal queries, and use email or a project management platform for formal announcements and documenting key decisions.
- Encourage Open Feedback: Foster a culture where team members feel safe to voice concerns and provide honest feedback. It's also important to understand how to overcome communication barriers to ensure your messages are received as intended.
By strategically managing communication, you eliminate information silos, boost team morale, and keep the project moving forward smoothly, making it an essential practice for any modern project manager.
3. Risk Management and Mitigation
Effective project management isn't just about planning for success; it's also about preparing for potential failures. Proactive risk management is the systematic process of identifying, analyzing, and responding to project risks to minimize their negative impact and capitalize on opportunities. This best practice turns uncertainty into a manageable variable, preventing unforeseen issues from derailing timelines and budgets.

This approach, championed by organizations like the Project Management Institute (PMI) and standardized in frameworks like ISO 31000, is crucial for complex initiatives. For example, NASA's rigorous risk management framework is fundamental to the success of its space missions, while construction projects like the London 2012 Olympics used it to stay on track despite immense complexity. By anticipating what could go wrong, teams can build resilience and agility into their project plan.
How to Implement This Practice
Integrating risk management involves creating a continuous cycle of identification, assessment, and response rather than a one-time check. It's a proactive mindset that must be embedded in the team's culture, especially in a remote setting where risks can be less visible.
- Create a Central Risk Register: This document is your single source of truth for all potential risks. It should list each risk, its potential impact, its probability of occurring, and the planned response.
- Involve the Entire Team: Encourage everyone, from developers to marketers, to contribute to risk identification. Diverse perspectives can uncover risks that might otherwise be missed. For a detailed guide on identifying and managing potential threats, learn how to conduct a comprehensive risk assessment.
- Develop Clear Mitigation Plans: For each significant risk, outline a specific plan of action. This could involve avoiding the risk, transferring it (e.g., through insurance), reducing its likelihood, or accepting it and having a contingency plan ready.
- Regularly Review and Update: Risks evolve as a project progresses. Schedule regular risk review meetings to discuss the status of known risks, identify new ones, and retire those that are no longer relevant.
By embedding this discipline into your workflow, you transform your team from being reactive to proactive, empowering them to navigate challenges with confidence and maintain project momentum. This is a hallmark of mature and successful project management.
4. Stakeholder Engagement and Management
A project’s success rarely depends solely on the project team; it hinges on effectively managing the expectations and influence of everyone impacted by the outcome. This is where stakeholder engagement and management becomes a critical project management best practice. This strategic process involves identifying, analyzing, and actively engaging with any individual or group that can affect or be affected by the project, ensuring their needs are understood and addressed throughout the project lifecycle.
Neglecting stakeholders can lead to roadblocks, scope changes, and a lack of buy-in, ultimately jeopardizing project goals. Methodologies like those from the Project Management Institute (PMI) and Agile frameworks emphasize this continuous dialogue. For example, involving customers in software development through user stories ensures the final product meets real-world needs, while a construction project requires constant community engagement to proceed smoothly.
How to Implement This Practice
Effective stakeholder management moves beyond simple communication; it requires a structured and empathetic approach to building and maintaining relationships, particularly with remote or distributed stakeholders.
- Create a Stakeholder Register: Begin by identifying all potential stakeholders, from the project sponsor and end-users to regulatory bodies and internal departments. Document their interests, influence, and expectations in a centralized register.
- Prioritize and Analyze: Not all stakeholders require the same level of attention. Use a tool like Mendelow's Matrix to categorize them based on their power and interest. This helps you focus your engagement efforts where they will have the most impact.
- Develop a Tailored Engagement Plan: Create specific communication and engagement strategies for different stakeholder groups. High-power, high-interest stakeholders may need frequent one-on-one meetings, while others might be kept informed through newsletters or status reports. For remote teams, understanding how to engage remote employees is crucial, as they are key internal stakeholders.
- Maintain Regular and Transparent Communication: Establish a consistent rhythm for updates and feedback sessions. Be transparent about project progress, challenges, and limitations to build trust and manage expectations realistically.
By systematically engaging stakeholders, you transform potential obstacles into powerful allies, creating a supportive environment that significantly increases the likelihood of project success.
5. Resource Planning and Allocation
Effective resource planning and allocation is a cornerstone of successful project delivery. This practice involves strategically identifying, scheduling, and distributing all necessary resources, including human talent, financial capital, and essential equipment, to ensure project tasks are completed efficiently. It is the art and science of putting the right resources on the right tasks at the right time, all while staying within budget and schedule constraints.
Without a solid resource plan, projects can quickly derail. Teams may face burnout from being overallocated, critical tasks can stall due to a lack of necessary skills or tools, and budgets can escalate unexpectedly. Methodologies like the Critical Path Method (CPM) and principles from Lean management highlight the importance of optimizing resource flow to prevent bottlenecks and maximize value. This is especially critical for remote and distributed teams where visibility into resource availability can be limited.
How to Implement This Practice
Strategic resource allocation moves beyond simply assigning people to tasks. It requires a forward-looking approach to balance demand with capacity, ensuring the project remains on a steady course from start to finish.
- Utilize Resource Management Tools: For modern teams, especially remote ones, spreadsheets are often insufficient. Employ specialized software to visualize resource capacity, track allocations in real-time, and forecast future needs. Many modern remote project management tools have built-in resource management features that provide a single source of truth for the entire team.
- Plan for Contingencies: Never allocate resources at 100% capacity. Build in buffers to account for unforeseen issues, sick days, or unexpected tasks. This proactive approach prevents a single delay from causing a domino effect across the entire project schedule.
- Develop Cross-Functional Capabilities: Encourage team members to develop skills in adjacent areas. A cross-functional team is more resilient and flexible, allowing you to reallocate personnel to address shifting priorities or cover temporary skill gaps without halting progress.
- Regularly Review and Adjust: A resource plan is not static. Hold regular review meetings, perhaps weekly or bi-weekly, to assess current allocations against project progress. Be prepared to use techniques like resource leveling (adjusting start/end dates) or smoothing (using slack) to resolve conflicts and optimize the plan.
By mastering resource planning, you transform your project from a reactive scramble into a well-oiled machine, ensuring that every asset contributes effectively toward achieving the project's goals. This methodical approach is a hallmark of high-performing project management.
6. Agile and Adaptive Project Management
Traditional project management often follows a rigid, linear path, but modern challenges demand a more flexible response. Agile and adaptive project management is an iterative approach that prioritizes collaboration, customer feedback, and the ability to pivot quickly. Instead of a single, long delivery cycle, projects are broken into smaller, incremental "sprints" or iterations, each delivering a piece of functional value.
This methodology, born from the Agile Manifesto and championed by pioneers like Jeff Sutherland, is designed to accommodate change rather than resist it. Companies like Spotify and Google have famously used agile principles to innovate rapidly. It is one of the most effective project management best practices for environments where requirements are evolving or not fully understood from the start, making it ideal for software development, product innovation, and complex problem-solving.
The following infographic illustrates the core iterative loop common in agile frameworks like Scrum.
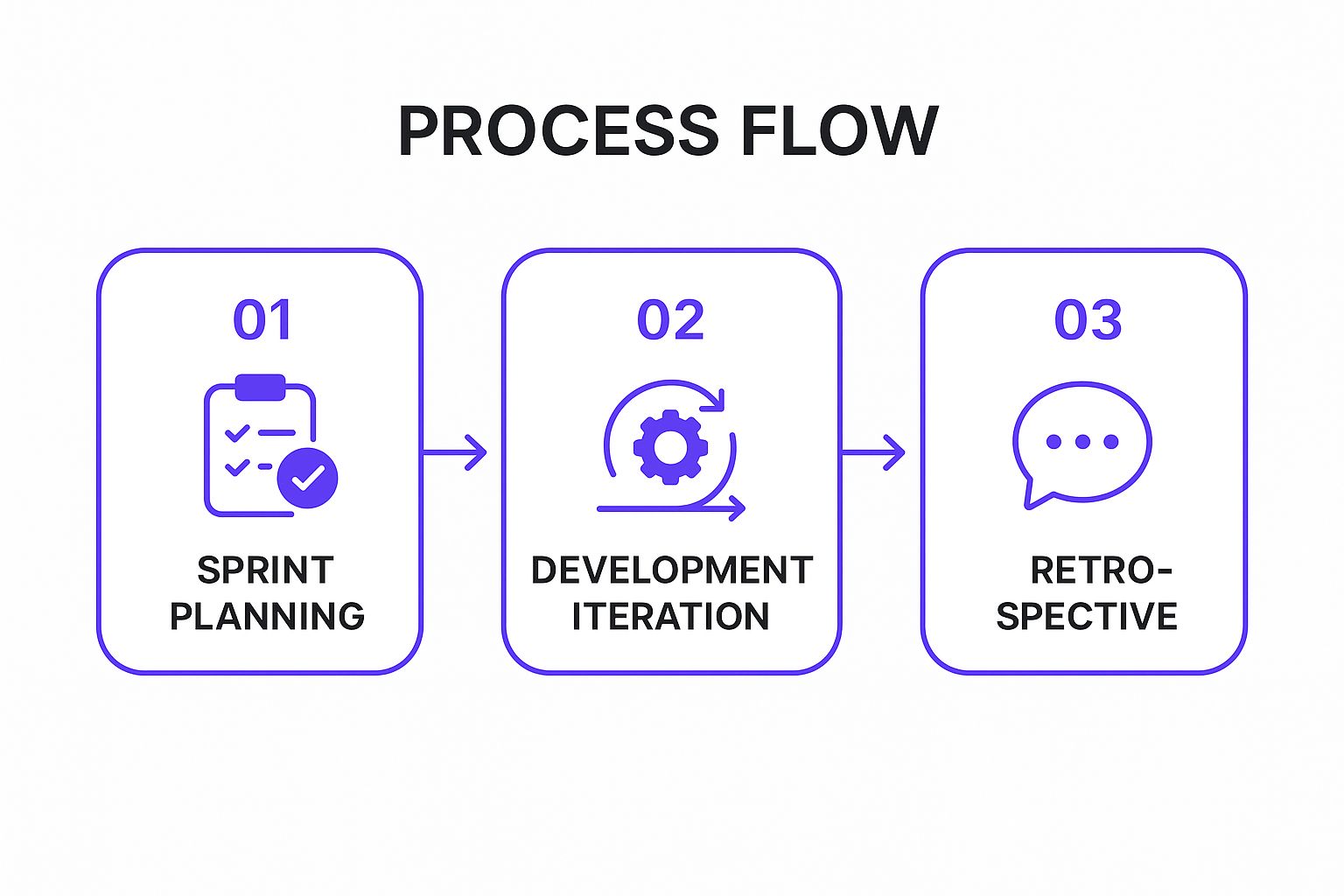
This simple yet powerful cycle of planning, executing, and reviewing ensures the team is constantly learning and realigning with stakeholder needs.
How to Implement This Practice
Adopting an agile mindset requires a cultural shift towards transparency, trust, and continuous improvement. It’s less about a rigid set of rules and more about embracing core principles.
- Start with a Pilot Project: Don't try to transform the entire organization overnight. Select a small, contained project to pilot agile methods. This allows the team to learn and adapt the process in a lower-risk setting.
- Invest in Training and Coaching: Agile frameworks like Scrum or Kanban have specific roles and ceremonies. Proper training for the team and stakeholders is crucial for success. An agile coach can help guide the team through early challenges.
- Focus on Delivering Value in Sprints: The goal of each iteration is to produce a tangible, potentially shippable increment of work. This keeps the team focused and provides regular opportunities for stakeholder feedback.
- Embrace a Learning Mindset: Not every sprint will be perfect. The retrospective meeting at the end of each cycle is a critical opportunity to discuss what went well, what didn't, and how to improve. Treat failures as valuable learning experiences.
Implementing these methods with geographically scattered teams presents unique challenges, but the rewards are significant. You can explore a deeper dive into making this work by learning more about managing distributed agile teams. By breaking down large projects into manageable sprints, remote teams can maintain momentum and alignment, proving that agile is a cornerstone of modern, successful project management.
7. Quality Management and Control
Integrating a robust quality management and control process is a non-negotiable project management best practice for delivering outcomes that meet or exceed stakeholder expectations. This practice involves systematically planning, executing, and monitoring activities to ensure that all project deliverables adhere to predefined quality standards. It moves beyond simply finding defects at the end; it's about embedding quality into every phase of the project lifecycle.
Pioneered by quality gurus like W. Edwards Deming and formalized in standards like ISO 9001, this approach prevents costly rework, enhances customer satisfaction, and protects brand reputation. In a remote or distributed team setting, a formal quality process is even more critical, as it provides a clear, objective framework for what "good" looks like, ensuring consistent output regardless of where team members are located.
How to Implement This Practice
Effective quality management is not an afterthought but a proactive strategy built into your project plan. It requires a structured approach to defining, measuring, and improving quality.
- Define Quality Criteria Early: Before work begins, collaborate with stakeholders to establish clear, measurable quality standards for each deliverable. What does success look like? What are the acceptance criteria? Document these in a quality management plan.
- Implement Quality Checkpoints: Don't wait until the end to check for quality. Build quality assurance activities, such as peer reviews, walkthroughs, and testing, into your project timeline at key milestones. This allows for early detection and correction of issues.
- Use a Mix of Control Methods: Combine automated testing tools for efficiency with manual reviews for nuanced, user-centric feedback. For example, a software team might use automated scripts to check code functionality while conducting manual usability tests to assess the user experience.
- Learn from Defects: Treat every defect or failure as a learning opportunity. Conduct root cause analysis to understand why an issue occurred and implement corrective and preventive actions to ensure it doesn't happen again.
By embedding quality management into your workflow, you create a culture of excellence where every team member feels responsible for the final outcome, solidifying its place as a cornerstone of modern project management.
8. Schedule Management and Time Planning
Effective schedule management and time planning are the disciplined processes of defining, sequencing, estimating, and controlling project activities to ensure timely completion. This practice involves creating a realistic timeline, setting milestones, and monitoring progress against that schedule. It is a cornerstone of project management best practices, transforming a project's goals into a time-bound action plan.
Without a well-managed schedule, projects drift, deadlines are missed, and costs escalate. Methodologies like the Critical Path Method (CPM) and tools like Gantt charts, pioneered by Henry Gantt, provide the structure needed to manage complex timelines. For distributed and remote teams, a clear, shared schedule is even more critical, serving as a single source of truth that aligns team members across different time zones.
How to Implement This Practice
Mastering your project's timeline requires more than just setting a due date. It is an ongoing process of estimation, tracking, and communication that keeps the entire project on track.
- Use Multiple Estimation Techniques: Don't rely on a single guess. Use methods like PERT (Program Evaluation and Review Technique) or three-point estimating (optimistic, pessimistic, and most likely) to create a more accurate and realistic forecast for task durations.
- Build in Buffer Time: Account for uncertainty and potential risks by incorporating buffers or contingency time into your schedule. This prevents unforeseen delays in one task from derailing the entire project timeline.
- Identify and Monitor the Critical Path: The critical path is the longest sequence of tasks that determines the project's minimum duration. Focus your monitoring efforts here, as any delay on this path directly impacts the project's completion date.
- Leverage Scheduling Software: For anything beyond simple projects, use tools like Microsoft Project, Asana, or Jira. These platforms help visualize timelines, manage dependencies, and make it easy to update and communicate schedule changes to all stakeholders, which is especially vital for remote teams.
9. Change Management and Control
No project exists in a vacuum; change is an inevitable part of the journey. One of the most critical project management best practices is establishing a systematic approach to change management and control. This involves creating a formal process to identify, evaluate, approve, and implement any modifications to the project's scope, timeline, or resources, ensuring that every adjustment is deliberate and controlled.
Without a formal change control system, projects are vulnerable to uncontrolled scope creep, confusion, and misalignment, especially in remote or distributed teams where informal requests can easily derail progress. Methodologies like ITIL and frameworks from the Project Management Institute (PMI) champion this practice to maintain project integrity, manage stakeholder expectations, and prevent chaos when priorities shift or new information emerges.
How to Implement This Practice
Effective change control is about balancing flexibility with structure. It allows for necessary adjustments while protecting the project's core objectives.
- Establish a Clear Process Early: Define and communicate a formal change request process from the project's outset. This process should detail how to submit a change, what information is required, who reviews it, and how decisions are communicated.
- Create a Change Control Board (CCB): For larger projects, form a CCB composed of key stakeholders, including the project sponsor, project manager, and technical leads. This group is responsible for evaluating the impact of proposed changes on cost, schedule, and quality before approving or rejecting them.
- Assess the Full Impact: Before approving a change, thoroughly analyze its direct and indirect consequences. For example, a seemingly minor feature request in a software project could have significant ripple effects on the system architecture, testing timelines, and team workload.
- Maintain a Detailed Change Log: Document every change request, its evaluation, the decision made, and its implementation status in a centralized change log. This log provides a transparent audit trail and is an invaluable communication tool for keeping all team members, especially those working remotely, informed.
By implementing a robust change control process, you empower your team to adapt to new requirements in an orderly fashion, ensuring the project remains on track and aligned with its strategic goals.
10. Performance Monitoring and Reporting
A cornerstone of effective project management best practices is the systematic process of performance monitoring and reporting. This involves continuously collecting, analyzing, and sharing project data against established baselines like scope, schedule, and budget. The goal is to track progress, identify deviations early, and provide stakeholders with the information they need to make timely, informed decisions.
Without consistent monitoring, a project operates in the dark, making it impossible to know if it's on track or headed for failure. This practice, central to frameworks like Earned Value Management (EVM) and Agile methodologies, turns raw data into actionable intelligence. For remote and distributed teams, transparent reporting builds trust and maintains alignment, ensuring everyone understands project health regardless of their location.
How to Implement This Practice
Effective reporting goes beyond simply sharing numbers; it's about telling a clear story about project performance. This requires a structured approach to data collection, analysis, and communication.
- Select Meaningful KPIs: Focus on key performance indicators (KPIs) that are truly actionable. Examples include Cost Performance Index (CPI), Schedule Performance Index (SPI), Agile burndown charts, and velocity tracking. Avoid vanity metrics that don't drive decisions.
- Automate Data Collection: Manually compiling reports is time-consuming and prone to error. Use project management tools to automate data collection and generate real-time dashboards, freeing up the team to focus on analysis and problem-solving rather than administrative tasks.
- Establish a Reporting Cadence: Define a regular schedule for reporting, such as weekly progress updates or monthly stakeholder briefings. A consistent rhythm ensures that information flows predictably and that issues are addressed proactively, not reactively.
- Visualize the Data: Use visual aids like charts, graphs, and dashboards to make complex information easy to understand at a glance. Visual reporting is especially powerful for quickly communicating trends and highlighting areas that require attention.
By integrating robust monitoring and reporting into your workflow, you create a feedback loop that drives continuous improvement and keeps the project aligned with its strategic objectives.
Top 10 Project Management Best Practices Comparison
| Aspect | Clear Project Charter & Scope Definition | Effective Communication Management | Risk Management & Mitigation | Stakeholder Engagement & Management | Resource Planning & Allocation | Agile and Adaptive Project Management |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Medium – Requires consensus and documentation | Medium – Ongoing coordination and tool usage | High – Continuous identification and analysis | Medium-High – Involves mapping and managing diverse interests | Medium-High – Needs forecasting and conflict resolution | High – Cultural and procedural shift required |
| Resource Requirements ⚡ | Moderate – Time for stakeholder involvement | Moderate – Time and communication platforms | High – Expertise and dedicated monitoring | Moderate – Time-intensive stakeholder engagement | Moderate-High – Tools and staff skills needed | Moderate – Skilled, cross-functional teams needed |
| Expected Outcomes 📊 | Clear direction, reduced scope creep, aligned expectations | Reduced conflicts, enhanced collaboration, informed decisions | Reduced surprises, better risk control, improved success rates | Increased support, better quality, reduced risks | Maximized efficiency, cost savings, better forecasting | Faster delivery, adaptability, increased customer satisfaction |
| Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Large/complex projects needing formal authorization | Projects with multiple stakeholders demanding info flow | High-risk projects requiring proactive management | Projects with diverse or influential stakeholder groups | Projects with limited resources and competing demands | Projects with evolving requirements and need for flexibility |
| Key Advantages ⭐ | Prevents ambiguity, improves approval, manages scope | Improves engagement, prevents silos, facilitates decisions | Proactive risk handling, resource optimization | Builds trust, reduces resistance, enhances decision-making | Optimizes resource use, reduces waste, supports timelines | Rapid value delivery, continuous improvement, team motivation |
Turning Best Practices into Project Success
You have just explored a comprehensive roundup of the ten most critical project management best practices, from crafting a clear project charter to mastering performance reporting. Navigating this landscape, especially within a remote or distributed team, can seem complex. However, these are not just theoretical concepts; they are the fundamental building blocks of repeatable, scalable, and predictable success. The journey from a good project manager to a great one is paved with the consistent application of these proven principles.
The core message threaded through each best practice is one of intentionality. Success is rarely accidental. It is the direct result of deliberate planning, transparent communication, proactive risk management, and a relentless focus on delivering value. When you formalize your processes around these pillars, you create a system that empowers your team, clarifies expectations for stakeholders, and builds resilience against the inevitable challenges every project faces.
From Theory to Action: Your Next Steps
Merely understanding these best practices is not enough. The true transformation occurs when you integrate them into your team's daily workflows. Here’s how to start turning these insights into tangible results:
- Start Small, Win Big: Don't try to implement everything at once. Select one or two practices that address your team's most significant pain points. Is scope creep a constant issue? Focus intensely on solidifying your Scope Definition and Change Management processes for the next project.
- Conduct a Retrospective: Use these ten best practices as a framework for a team retrospective. Ask yourselves: "Where are we strong? Where are our biggest gaps?" This collaborative audit will generate buy-in and create a shared sense of ownership over the improvement process.
- Standardize Your Toolkit: Ensure your project management software and communication tools are aligned with these practices. Configure your tools to support clear task assignments, risk tracking, and transparent progress reporting. A well-configured tool becomes a powerful enabler of best-practice execution.
The True Measure of Progress
Ultimately, the goal of adopting these project management best practices is to drive better outcomes. This means delivering projects on time, within budget, and to the required quality standards. But how do you know if your new approach is truly working? To truly gauge the impact of implemented best practices, it is essential to understand how to effectively measure project success. This involves setting clear key performance indicators (KPIs) and tracking them diligently, connecting your team's daily efforts to tangible business value.
Mastering these practices creates a powerful ripple effect. It reduces team burnout by minimizing confusion and rework. It builds trust with stakeholders by providing them with clear visibility and predictable results. Most importantly, it fosters a culture of excellence and continuous improvement, where every team member is empowered to contribute their best work. This journey is not a one-time fix but a sustained commitment to building a more efficient, resilient, and successful project engine. The effort you invest today will pay dividends in every project you launch tomorrow.
Ready to supercharge your team's initial brainstorming and set the stage for project success? Bulby uses an AI-guided process to help remote teams generate better ideas, ensure every voice is heard, and build a strong foundation from day one. Start your next project with clarity and confidence by trying Bulby today.

