Igniting Your Business Creativity: A Guide to Effective Brainstorming
Need fresh business ideas? This listicle provides seven proven brainstorming methods to fuel your team's creativity and generate winning concepts. Whether you're a remote startup or an established tech team, learning how to brainstorm effectively is crucial for success. Discover how techniques like Mind Mapping, the SCAMPER technique, and the Six Thinking Hats method can help you unlock innovative solutions. We'll also explore how to brainstorm ideas for a business using approaches like the Business Model Canvas and trend analysis. Boost your brainstorming sessions and achieve remarkable results in 2025 and beyond.
1. Classic Brainstorming (Osborn Method)
When it comes to brainstorming ideas for a business, especially in the fast-paced world of remote teams and startups, the Classic Brainstorming method, also known as the Osborn Method, remains a powerful tool. Developed by Alex Osborn in the 1940s, this technique prioritizes quantity over quality in the initial stages, encouraging a free-flowing exchange of ideas without the constraints of immediate judgment or feasibility assessments. This approach is particularly beneficial for remote teams as it can foster a sense of collaborative energy and generate a wide range of potential business ventures. It leverages the collective intelligence of the team, allowing for a diverse pool of perspectives to contribute to the innovation process.
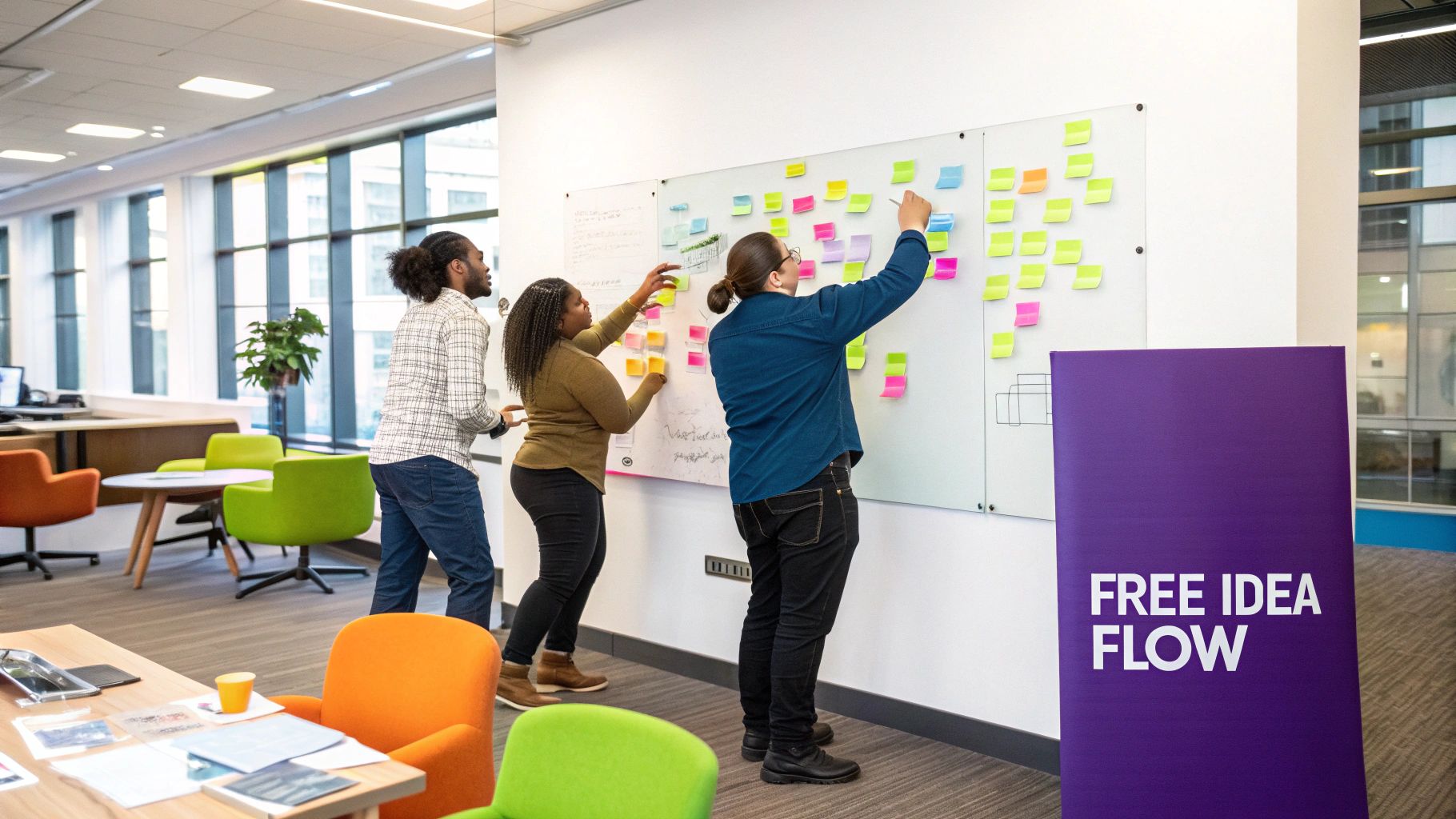

The Osborn Method operates on a few core principles. First, it emphasizes generating a large volume of ideas within a set timeframe. This encourages participants to think outside the box and explore unconventional avenues. Second, it suspends all criticism during the idea generation phase. This creates a psychologically safe environment where team members feel comfortable sharing even seemingly outlandish ideas without fear of ridicule. Third, it encourages building upon and combining existing ideas. This collaborative element can spark unexpected connections and lead to innovative solutions that wouldn't have emerged from individual brainstorming. This is particularly relevant for remote tech teams, where individuals may be working across different time zones and require asynchronous collaboration tools to effectively build upon each other's ideas.
The benefits of this method are numerous. For remote teams, it can be a highly effective way to build team cohesion and engagement, combating the potential isolation of remote work. The inclusive nature of the process ensures that all voices are heard, regardless of location or personality type. It also facilitates rapid idea generation, crucial for startups operating in dynamic markets. This speed is especially advantageous for remote startups looking to iterate quickly and respond to market changes efficiently.
However, the Osborn Method also has potential drawbacks. Dominant personalities can sometimes steer the conversation, hindering the contributions of quieter team members. The emphasis on quantity can also lead to a large number of impractical or low-quality ideas, requiring a rigorous filtering process later on. Social loafing, where individuals contribute less in a group setting, can be a challenge, especially in larger remote teams. Finally, the lack of initial feasibility assessment can lead to time being spent on ideas that are ultimately unviable.
Despite these potential downsides, the Osborn Method has a proven track record of success. IDEO, a renowned design consultancy, utilizes variations of this method in their design thinking sessions for product innovation. 3M's innovation workshops, which famously led to the invention of Post-it Notes, are another testament to the power of this approach. Even tech giants like Google have employed similar principles with their "20% time" projects, which resulted in innovations like Gmail and AdSense. These examples demonstrate the method's effectiveness across diverse industries and team structures, making it a valuable tool for brainstorming ideas for a business, especially in a remote setting.
To effectively implement the Osborn Method for your remote team or startup, consider these tips:
- Keep groups small (5-8 people): This ensures active participation from all members and prevents the discussion from becoming unwieldy in a virtual setting.
- Use a skilled facilitator: A facilitator can guide the discussion, ensure everyone contributes, and enforce the "no judgment" rule.
- Set clear time limits and objectives: This helps maintain focus and productivity during the session.
- Create a comfortable, judgment-free environment: Emphasize psychological safety and encourage open sharing of ideas, regardless of how unconventional they may seem. Utilize online collaboration tools that allow for anonymous idea submission if necessary.
- Document all ideas visually: Use virtual whiteboards or shared documents to capture all generated ideas in a way that is accessible to all team members.
- Follow up with evaluation sessions: After the initial brainstorming phase, schedule separate sessions dedicated to evaluating and prioritizing the generated ideas.
The Osborn Method is a valuable tool for brainstorming ideas for a business, especially for remote teams and startups. Its simplicity, collaborative nature, and potential for generating a large volume of ideas make it a worthwhile approach for any team looking to unlock their creative potential and drive innovation.
2. SCAMPER Technique
When brainstorming ideas for a business, especially as a remote team, it's easy to get stuck in a rut or feel limited by distance. The SCAMPER technique offers a structured and powerful way to overcome these challenges and generate innovative business ideas, whether you're a remote tech team developing a new app or a remote startup looking for its next big break. This method utilizes seven thought-provoking prompts – Substitute, Combine, Adapt, Modify/Magnify, Put to other uses, Eliminate, and Reverse/Rearrange – to spark creativity and unlock new possibilities. It provides a framework for systematic thinking, making it particularly valuable for remote teams who need to collaborate effectively despite geographical separation.

Essentially, SCAMPER provides a checklist of questions to ask about your existing product, service, or even a competitor's offering. By systematically working through each prompt, you can uncover hidden opportunities and generate a wealth of new ideas. For instance, consider the "Substitute" prompt. What materials, processes, or components could you substitute in your current product to improve it, reduce costs, or reach a new market? Remote teams can benefit significantly from this structured approach, as it helps maintain focus and ensures everyone contributes effectively to the brainstorming process.
Let's break down each letter of the SCAMPER technique:
- Substitute: What can you substitute in your product, service, or process? Consider materials, components, people, or even the marketing approach.
- Combine: Can you combine your offering with another product, service, or technology to create something new and valuable? This is particularly relevant for remote tech teams exploring integrations and partnerships.
- Adapt: What can you adapt from other industries or businesses to improve your offering? This could involve adapting a successful business model or a specific feature.
- Modify/Magnify: Can you modify or magnify any aspect of your product or service? Think about changing its size, shape, features, or even its target audience.
- Put to other uses: Can your product or service be used in a different way or for a different purpose? This can open up entirely new market segments.
- Eliminate: What can you eliminate from your product, service, or process to simplify it, reduce costs, or improve efficiency? Remote startups often benefit from this by streamlining operations and focusing on core value propositions.
- Reverse/Rearrange: Can you reverse or rearrange any aspect of your product, service, or process? This can lead to unexpected breakthroughs and innovative solutions.
The SCAMPER technique has fueled the success of many well-known businesses. Netflix utilized the “Substitute” prompt when it replaced physical DVDs with online streaming, revolutionizing the entertainment industry. Uber “Combined” the traditional taxi service with mobile app technology, creating a global ride-hailing giant. Airbnb “Adapted” the concept of hotels to private homes, disrupting the hospitality sector. These examples showcase the transformative power of SCAMPER in generating disruptive business ideas.
Here are some tips for using SCAMPER effectively in your remote brainstorming sessions:
- Work through each letter systematically: Don’t skip any prompts, even if they seem irrelevant at first. You never know where a hidden gem of an idea might be lurking.
- Ask multiple questions for each prompt: The more questions you ask, the more possibilities you'll uncover. Encourage your remote team members to contribute their unique perspectives.
- Use existing successful businesses as starting points: Analyze how other companies have used SCAMPER and consider how you can apply similar principles to your own business.
- Combine SCAMPER with other brainstorming methods: SCAMPER can be a powerful standalone tool, but it can also be combined with other techniques like mind mapping or SWOT analysis to generate even more comprehensive results.
- Document insights from each prompt: Use a shared document or online whiteboard to capture all the ideas generated during the brainstorming session. This ensures that no valuable insights are lost and provides a reference point for future development.
- Apply to different aspects of your business: Don't limit yourself to just the product or service. Use SCAMPER to brainstorm ideas for marketing, operations, customer service, and other areas of your business.
While SCAMPER provides a robust framework, it’s important to be aware of its limitations. It might feel restrictive to some, and it requires an existing reference point to work effectively. Overuse can also lead to formulaic thinking. However, its benefits in providing structure and overcoming mental blocks, particularly within remote teams, significantly outweigh these drawbacks. By implementing SCAMPER strategically, you can equip your remote team with a powerful tool for generating innovative business ideas and driving success in today's competitive landscape.
3. Mind Mapping
When brainstorming ideas for a business, especially in the fast-paced world of remote teams, startups, and tech companies, finding a method that fosters creativity and collaboration is crucial. Mind mapping is a powerful visual brainstorming technique that can unlock innovative thinking and help your team generate a wealth of business ideas. It starts with a central business theme and branches out into related subtopics, concepts, and potential opportunities, much like the branches of a tree. This approach allows for a more organic and free-flowing exploration of ideas compared to traditional linear brainstorming methods.
Mind mapping uses colors, images, and keywords to create a spider-web-like diagram. This visual representation maps the relationships between different business concepts, fostering a deeper understanding of how ideas connect and potentially revealing hidden opportunities. The hierarchical structure, moving from general concepts at the center to more specific ideas on the branches, helps organize the brainstorming process, making it easier to analyze and prioritize potential business ventures. This is particularly beneficial for remote teams who might find traditional brainstorming sessions less engaging or productive.
Think of companies like Virgin Group, Disney, Amazon, and Tesla. Virgin's expansion across diverse industries, Disney's intricate content ecosystem, Amazon's journey from online books to cloud computing, and Tesla's integrated approach to batteries, solar energy, and transportation—all of these could have benefitted from mind mapping to visualize and strategize their growth. For example, imagine Disney using a mind map to explore the potential connections between a popular animated character and new theme park attractions, merchandise, or even streaming series.
Here are some actionable tips to make mind mapping effective for brainstorming ideas for a business:
- Start with a broad business category at the center: For example, if you're a remote tech team, your central topic might be "Remote Collaboration Software" or "AI-Powered Productivity Tools."
- Use single keywords or short phrases rather than long sentences: This keeps the map clean and easy to understand.
- Employ different colors for different business categories or subtopics: This visual cue helps differentiate and organize information quickly.
- Include both problems and potential solutions on the map: This fosters a more comprehensive understanding of the business landscape and opportunities.
- Use digital tools like MindMeister or XMind for seamless collaboration, especially for remote teams: This enables real-time contributions and ensures everyone is on the same page.
- Review and refine the map over multiple sessions: This allows for deeper exploration and refinement of ideas.
- Consider both the market needs and your team's strengths when adding branches: This ensures that the generated ideas are not only creative but also viable and feasible.
While mind mapping offers significant advantages, it's important to be aware of its limitations. It can become cluttered and difficult to interpret if too many ideas are crammed onto a single map. For highly linear thinkers, the non-linear nature of mind mapping might feel less intuitive. Creating a detailed mind map can also be time-consuming, and maximizing its visual impact often requires some artistic flair. For very simple business ideas, a mind map might be overkill.
However, the pros generally outweigh the cons. Mind mapping engages both logical and creative thinking, making it an ideal brainstorming method for remote tech teams and startups seeking innovative solutions. The visual nature makes complex relationships readily visible and understandable, simplifying communication and collaboration. It's easy to add new ideas and make connections as they arise organically during brainstorming sessions. Learn more about Mind Mapping for specific examples and further guidance. The technique works particularly well for visual learners and can reveal unexpected connections and business opportunities that might be missed using traditional brainstorming methods. Its use has been popularized by figures like Tony Buzan, a British author and mind mapping pioneer, and its roots can even be traced back to historical figures like Leonardo da Vinci and his use of visual note-taking. Today, design thinking practitioners at institutions like the Stanford d.school continue to champion the power of visual thinking and mind mapping for innovation.
4. Problem-Solution Brainstorming
When brainstorming ideas for a business, a laser-focused approach can often yield the most promising results. Problem-solution brainstorming flips the script on traditional ideation. Instead of starting with a product or service idea, you begin by identifying a problem, pain point, or unmet need within a specific market. Then, you generate business ideas specifically designed to address that problem. This method ensures that your brainstormed business concepts have inherent market demand and offer a clear customer value proposition, a crucial factor for remote startups, remote tech teams, and remote teams in general. It's a particularly valuable approach for those working remotely, as it encourages a data-driven approach to idea generation, reducing the reliance on chance encounters and water cooler conversations that are often absent in distributed teams.
This approach works by first deeply understanding the target market. This understanding goes beyond simple demographics and delves into the daily frustrations, challenges, and unfulfilled desires of potential customers. Once a significant problem is identified, the brainstorming process shifts to developing potential solutions. This solution-oriented thinking inherently builds in market validation, as the business concept is directly tied to a pre-existing need. For example, imagine a remote tech team struggling with asynchronous communication. Instead of brainstorming random software ideas, they could identify the core problems: difficulty tracking project updates, inefficient meeting scheduling across time zones, or a lack of clear documentation. By focusing on these specific problems, the team is more likely to develop a software solution with genuine market appeal within the remote work community.
Numerous successful businesses have been built on this foundation. Spanx, for instance, directly addressed women's undergarment problems with innovative shapewear solutions. Dropbox tackled the pervasive issues of file sharing and storage in an increasingly digital world. Square revolutionized payment processing for small businesses by simplifying transactions and hardware. Peloton identified the desire for convenient and engaging home fitness and combined it with the energy of live classes, creating a highly successful business model. These are all prime examples of how identifying a real-world problem and providing an effective solution can lead to significant business success.
Want to put this method into action? Here are some actionable tips for effective problem-solution brainstorming:
- Interview potential customers about their daily frustrations: Directly engaging with your target market is invaluable. Ask open-ended questions to understand their workflows, pain points, and desired outcomes. For remote teams, this could involve surveying other remote workers about their biggest challenges.
- Observe people in their natural environments (or their virtual ones): Pay attention to how people interact with products and services, both online and offline. Identify areas of friction or inefficiency. For remote tech teams, observe how colleagues navigate online collaboration tools.
- Research online forums and complaint sites: These platforms are goldmines of unfiltered customer feedback. Explore discussions related to your target market to uncover common problems and unmet needs.
- Focus on problems you personally experience: Sometimes the best business ideas come from solving your own frustrations. If you're struggling with something as a remote worker, chances are others are too.
- Consider problems in rapidly changing industries: Industries undergoing significant disruption often present numerous opportunities for innovative problem-solving. Think about the impact of remote work on traditional office practices.
- Look for problems that affect large numbers of people: While niche markets can be profitable, addressing widespread problems significantly increases your potential customer base.
Problem-solution brainstorming offers several compelling advantages: it creates businesses with clear value propositions, increases the likelihood of market acceptance, simplifies the process of validating business concepts, prioritizes customer needs over personal interests, and enables you to identify underserved market segments. However, it's important to also acknowledge potential drawbacks. It may limit breakthrough innovation by focusing on existing problems, potentially leading to incremental rather than disruptive ideas. This method also requires thorough market research and customer insight to be effective. Furthermore, it might overlook problems people don’t know they have and can be constrained by current problem awareness.
When brainstorming ideas for a business, problem-solution brainstorming shines as a particularly practical and effective method, especially for remote teams. By grounding your ideas in real-world problems, you drastically increase the chances of developing a product or service that resonates with the market and ultimately achieves success. The pioneers of this approach, including Steve Blank with his customer development methodology, Eric Ries and his Lean Startup problem validation, Clayton Christensen and his jobs-to-be-done theory, and Sara Blakely, founder of Spanx and a problem-solving advocate, demonstrate the power of this approach. Learn more about Problem-Solution Brainstorming to further refine your understanding and application of this valuable technique.
5. Six Thinking Hats: A Structured Approach to Brainstorming Ideas for a Business
When brainstorming ideas for a business, especially within a remote team, it's easy to get caught up in a whirlwind of opinions and perspectives. A structured approach can help channel that energy productively. That’s where Edward de Bono's Six Thinking Hats method comes in. This powerful technique uses six metaphorical hats, each representing a different mode of thinking, to guide your brainstorming sessions and ensure a comprehensive evaluation of your business ideas. This method is particularly valuable for remote teams, remote tech teams, and remote startups, offering a framework for structured discussions that can be challenging in a virtual environment.
The Six Thinking Hats utilizes six distinct colors, each symbolizing a specific perspective: White (facts and information), Red (intuition and emotion), Black (caution and critical thinking), Yellow (optimism and benefits), Green (creativity and new ideas), and Blue (process and control). By systematically rotating through these “hats,” teams can examine business ideas from every angle, promoting a balanced and thorough analysis. This structured approach helps overcome some of the challenges of remote brainstorming, ensuring that everyone has a chance to contribute and that no critical perspective is overlooked.
How it Works:
The Six Thinking Hats process involves sequentially focusing on each thinking mode. The team starts with the Blue Hat to define the problem and set the agenda for the session. Then, they might move to White Hat to gather relevant data and information. Next, the Green Hat could be used to generate innovative solutions. The Yellow Hat explores the positive aspects of those ideas, while the Black Hat assesses potential risks and challenges. Finally, the Red Hat allows for the expression of gut feelings and intuitions. The process concludes with the Blue Hat to summarize the discussion and decide on the next steps.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
Large corporations like IBM, McKinsey & Company, and Procter & Gamble have incorporated structured thinking approaches, including variations of the Six Thinking Hats, into their innovation labs, strategic planning sessions, and product development processes. Government policy development workshops also utilize these techniques for comprehensive analysis and decision-making. These examples demonstrate the versatility and effectiveness of the Six Thinking Hats method across various industries and applications.
Actionable Tips for Remote Teams:
- Use all six hats for each business idea: Ensure a comprehensive perspective.
- Spend equal time in each thinking mode: Avoid overemphasizing certain aspects.
- Have a facilitator guide transitions between hats: Maintain focus and momentum.
- Document insights from each hat perspective: Create a record of the discussion.
- Use the Blue Hat to manage the overall process: Set clear objectives and ensure effective time management.
- Practice with simple topics before tackling complex business planning: Familiarize the team with the method.
Pros:
- Ensures comprehensive analysis of business ideas
- Reduces conflict by separating thinking types
- Encourages participation from diverse personality types
- Provides structure for complex business discussions
- Helps identify potential issues early in the planning phase
Cons:
- Can feel artificial or forced initially
- Requires facilitator training for effective use
- May slow down fast-paced brainstorming sessions
- Some individuals may resist the structured approach
- Can become mechanical if not used thoughtfully
The following infographic visualizes a simplified three-step process within the Six Thinking Hats method, focusing on the flow from gathering information to generating ideas and then analyzing risks.
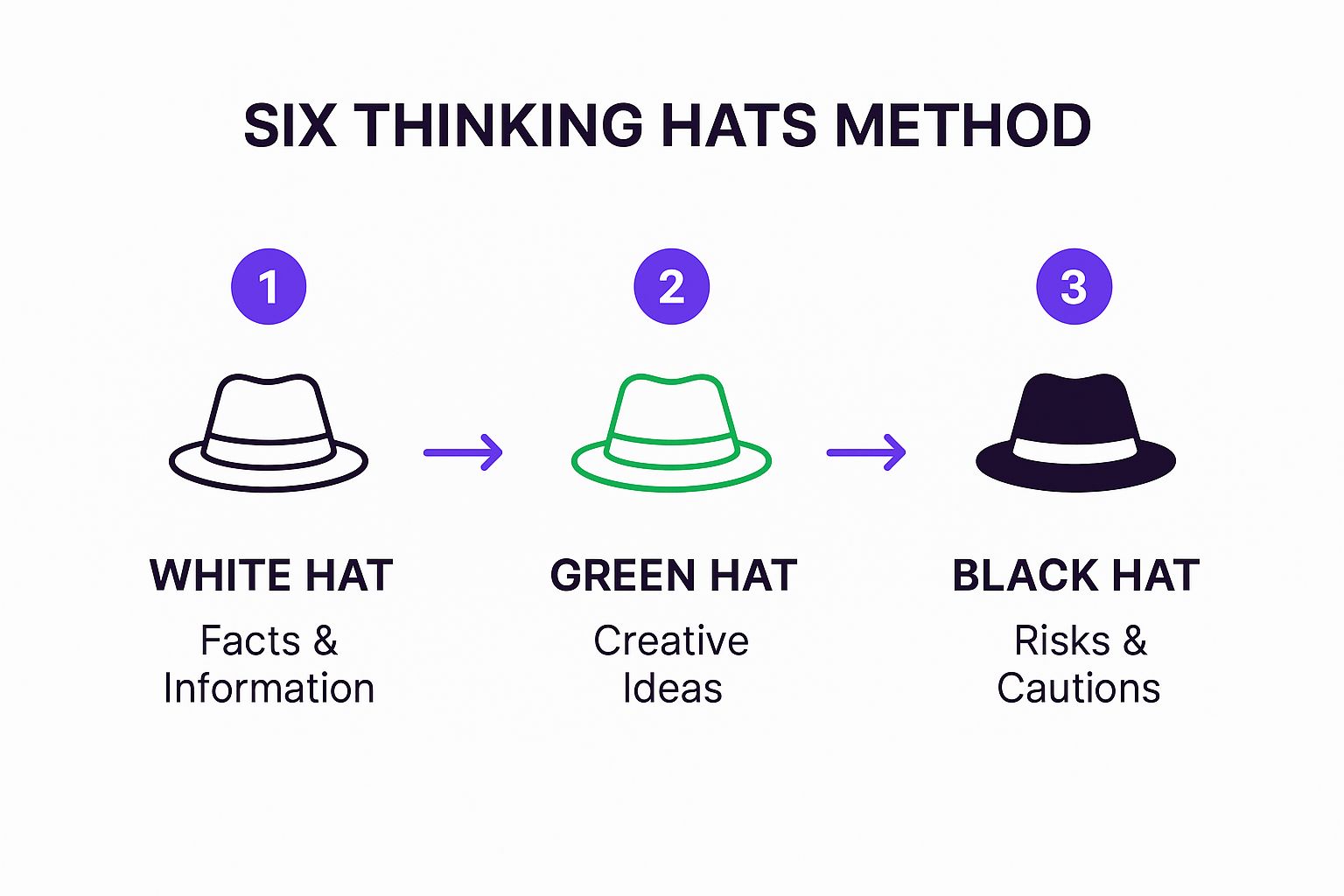
The infographic illustrates the sequential flow from objective information gathering (White Hat) to creative idea generation (Green Hat) and finally to critical risk assessment (Black Hat). This highlights the importance of building upon each stage, ensuring that creative solutions are grounded in facts and thoroughly vetted for potential pitfalls.
The Six Thinking Hats method deserves its place in this list because it provides a robust and structured framework for brainstorming ideas for a business, particularly beneficial for remote teams navigating the complexities of virtual collaboration. By encouraging a holistic and balanced perspective, this technique helps teams generate innovative ideas, mitigate potential risks, and make informed decisions. Learn more about Six Thinking Hats. This resource can provide further insights into implementing creative thinking exercises for your remote team.
6. Trend Analysis and Future-Casting
When brainstorming ideas for a business, looking toward the future can unlock innovative and potentially disruptive concepts. Trend analysis and future-casting is a forward-looking brainstorming approach that allows you to anticipate market needs before they become obvious, giving you a potential first-mover advantage. This method goes beyond simply identifying current trends; it delves into emerging trends, technological advancements, demographic shifts, and cultural changes to paint a picture of future opportunities. For remote teams, remote tech teams, and remote startups, this approach is particularly valuable as it can help identify emerging niches in the digital landscape.
This method involves examining "weak signals"—subtle hints of change that often go unnoticed—across multiple categories, including technological, social, economic, environmental, and political landscapes. Instead of focusing on the present, you're looking 5, 10, even 20 years ahead, anticipating how these evolving trends might converge to create entirely new markets. By considering a longer time horizon, you can identify potential disruptions and position your business to capitalize on them.
Imagine trying to brainstorm ideas for a business in the early 2000s. If you had employed trend analysis and future-casting, you might have noticed the increasing miniaturization of technology, the growing accessibility of the internet, and the nascent desire for on-demand services. These weak signals could have led you to an idea like developing a mobile app for ordering food delivery, years before the likes of DoorDash became household names. This illustrates the power of anticipating future needs.
Features of Trend Analysis and Future-Casting:
- Focus on Emerging Trends and Weak Signals: Don't just look at what's popular now. Dig deeper to uncover the subtle indicators of what will be popular in the future.
- Multiple Trend Categories: Consider trends across a broad spectrum, from technological advancements to shifts in societal values.
- Time Horizon Planning (5-20 years ahead): Think long-term. Where are these trends leading us in the coming decades?
- Cross-Industry Trend Application: A trend in one industry can often inspire innovation in another.
- Scenario Planning and Future Visioning: Develop multiple potential future scenarios based on different trend combinations.
Pros:
- First-Mover Advantage: Be the first to market with a new product or service catering to an emerging need.
- Future-Proofing: Avoid investing in businesses that may become obsolete due to technological or societal changes.
- Innovative Concepts: Generate truly novel and forward-thinking business ideas.
- Less Competition: Emerging markets offer less competition than established ones.
- Alignment with Long-Term Societal Changes: Position your business to benefit from long-term shifts in demographics, values, and lifestyles.
Cons:
- High Uncertainty: Predicting the future is inherently difficult.
- Premature Market Entry: The market may not be ready for your innovative idea.
- Resource Intensive: Requires significant research, analysis, and expertise.
- Risk of Misjudgment: You might bet on the wrong trends.
- Missed Current Opportunities: Focusing on the future may cause you to overlook profitable opportunities in the present.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- Tesla: Anticipated the growing demand for electric vehicles.
- Beyond Meat: Capitalized on the increasing popularity of plant-based diets.
- Zoom: Prepared for the rise of remote work and virtual communication.
- DoorDash: Leveraged the growth of the on-demand economy.
Tips for Applying Trend Analysis and Future-Casting:
- Follow Trend Research Organizations: Stay updated on emerging trends by following organizations like TrendWatching.
- Study Demographic Data: Understand how generational shifts and population changes are shaping the future.
- Monitor Emerging Technologies: Keep an eye on innovations coming out of research labs and universities.
- Observe Lifestyle Changes in Leading-Edge Markets: Look to cities and countries known for early adoption of new trends.
- Consider Convergence of Multiple Trends: Analyze how different trends might intersect and create new opportunities.
- Validate Trends Through Multiple Sources and Experts: Don't rely on a single source. Consult multiple experts and data points.
Popularized By:
- Faith Popcorn (Trend forecaster and futurist)
- Ray Kurzweil (Technology futurist)
- TrendWatching (Global trend firm)
- MIT Technology Review (Emerging technology analysis)
While brainstorming ideas for a business, especially within the remote work landscape, trend analysis and future-casting offer a powerful way to identify groundbreaking opportunities. While it requires significant effort and carries inherent risks, the potential rewards of tapping into future markets are substantial. For remote teams and startups, leveraging these techniques can help position them at the forefront of the digital revolution, creating innovative solutions for the future of work.
7. Business Model Canvas Brainstorming
When brainstorming ideas for a business, especially as a remote team, a structured approach can be invaluable. The Business Model Canvas (BMC) offers just that. This strategic management template provides a visual, one-page overview of a business's key components, making it easier for remote tech teams and startups to collaboratively brainstorm, refine, and validate their business model. This method stands out in brainstorming sessions because it ensures everyone is on the same page, literally, and working towards a shared understanding of how the business will function and create value.
Developed by Alexander Osterwalder and Yves Pigneur, the BMC lays out nine interconnected building blocks that encompass all essential aspects of a business. It's particularly powerful for brainstorming ideas for a business because it moves beyond just the product and forces you to consider the entire ecosystem surrounding it. By visually mapping out these blocks, remote teams can gain a holistic perspective of their business idea and identify potential strengths, weaknesses, and areas for innovation. Let's delve into each component:
- Customer Segments: Who are your target customers? What are their needs and characteristics? Defining your customer segments helps tailor your value proposition and marketing efforts.
- Value Propositions: What unique value do you offer your customers? How do you solve their problems or fulfill their needs? This is the core of your business offering.
- Channels: How do you reach your customer segments? What distribution channels will you use (e.g., online advertising, social media, direct sales)?
- Customer Relationships: What type of relationship do you establish and maintain with each customer segment? This can range from personal assistance to automated interactions.
- Revenue Streams: How do you generate revenue from each customer segment? What are your pricing models and payment methods?
- Key Activities: What key activities must your business perform to deliver its value propositions? This might include software development, content creation, or logistics.
- Key Resources: What essential resources do you need to execute your key activities? These can be physical, intellectual, human, or financial.
- Key Partnerships: Which key partners and suppliers do you need to support your business model? Strategic alliances can enhance your capabilities and reach.
- Cost Structure: What are the most important costs inherent in your business model? Understanding your cost drivers helps determine profitability and pricing strategies.
The beauty of the BMC lies in its visual representation. Using a single canvas, either physical or digital (tools like Miro and Mural work well for remote teams), teams can write down ideas on sticky notes for each block. This allows for easy rearranging, grouping, and iterating as the brainstorming session progresses. The visual layout facilitates a shared understanding and encourages discussion, making it particularly effective for remote teams brainstorming ideas for a business.
Successful examples of the BMC in action are abundant. Airbnb leveraged the platform business model, connecting travelers with hosts. Netflix disrupted the entertainment industry by transitioning from a DVD rental service to a subscription-based streaming platform. Freemium models, used by Spotify and LinkedIn, offer basic services for free while charging for premium features. Amazon exemplifies a marketplace and ecosystem approach, connecting buyers and sellers and offering a vast range of services.
Here are some tips for maximizing the effectiveness of a BMC brainstorming session:
- Start with customer segments and value propositions: Understanding your target customer and the value you offer is fundamental.
- Use sticky notes: This facilitates easy movement and iteration of ideas, especially in a virtual setting.
- Brainstorm multiple options for each block: Don't limit yourself to a single idea. Explore different possibilities.
- Look for innovative combinations across blocks: How can different elements of your business model reinforce each other to create a unique and compelling offering?
- Test assumptions with potential customers: Validate your ideas with your target audience to ensure you're building something people want.
- Consider how the blocks reinforce each other: A strong business model has interconnected elements that work together seamlessly.
While the BMC offers numerous advantages, it’s important to be aware of its potential drawbacks. It can be overwhelming for very simple business ideas, and the framework may unintentionally constrain thinking if not used flexibly. It requires a basic understanding of business model concepts, and working through all nine blocks thoroughly takes time. Additionally, the BMC might not capture all industry-specific nuances.
Despite these limitations, the BMC remains a powerful tool for brainstorming ideas for a business, especially for remote tech teams and startups. Its structured approach, visual representation, and emphasis on interconnectedness make it a valuable asset in developing and refining a robust and innovative business model. For more information and resources, you can visit Strategyzer, a platform dedicated to business model innovation (strategyzer.com).
7 Brainstorming Strategies Comparison
| Brainstorming Strategy | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classic Brainstorming (Osborn) | Low to Moderate 🔄 | Minimal, just group and facilitator ⚡ | Large volume of varied ideas 📊 | Early idea generation, team engagement | Encourages creativity and collaboration ⭐ |
| SCAMPER Technique | Moderate 🔄 | Low to Moderate, requires prompts & prep ⚡ | Systematic, diverse innovation insights 📊 | Refining existing ideas, overcoming mental blocks | Clear framework for structured creativity ⭐ |
| Mind Mapping | Moderate 🔄 | Low to Moderate, tools or pen & paper ⚡ | Visualized connections, insights 📊 | Exploring complex relationships, visual thinking | Engages both logical and creative thinking ⭐ |
| Problem-Solution Brainstorming | Moderate 🔄 | Moderate, needs customer research ⚡ | Focused, validated business ideas 📊 | Customer pain points, market-driven innovation | Produces market-relevant, value-driven ideas ⭐ |
| Six Thinking Hats | Moderate to High 🔄 | Moderate, facilitator and training needed ⚡ | Comprehensive idea evaluation 📊 | Balanced decision-making, complex problem analysis | Encourages diverse thinking styles, reduces conflict ⭐ |
| Trend Analysis & Future-Casting | High 🔄 | High, requires research & expert input ⚡ | Forward-looking, innovative opportunities 📊 | Long-term planning, emerging market identification | Anticipates future trends and market shifts ⭐ |
| Business Model Canvas | Moderate 🔄 | Moderate, collaborative team effort ⚡ | Holistic business model insights 📊 | Business model innovation, startup planning | Comprehensive business logic visualization ⭐ |
Unleashing the Power of Brainstorming: Fueling Your Business Forward
From classic brainstorming sessions using the Osborn method to forward-thinking trend analysis and future-casting, exploring diverse approaches is key to generating innovative business ideas for a business. This article highlighted powerful techniques like SCAMPER, mind mapping, and the Six Thinking Hats method, all designed to unlock your team's creative potential. Remember, the most effective brainstorming sessions aren't just about the quantity of ideas; they're about fostering a collaborative environment where every team member, especially in remote tech teams and startups, feels empowered to contribute. Mastering these brainstorming ideas for a business is invaluable for navigating today's rapidly changing market, enabling your team to develop groundbreaking solutions and drive your business towards lasting success.
For remote teams looking to supercharge their brainstorming sessions and seamlessly implement these techniques, consider exploring Bulby. Bulby provides structured frameworks and facilitates dynamic remote team interactions, making it easier than ever to generate, refine, and implement winning business ideas for a business. Ready to ignite your team's creativity and unlock your full potential? Visit Bulby and start your free trial today!

