Let's be honest, many people picture innovation as a lightning bolt of inspiration—a sudden "eureka!" moment that strikes out of nowhere. But that's a myth. In reality, innovation is a process. It’s a structured journey that takes a spark of an idea and carefully develops it into something with real-world value. Getting this distinction right is the first step for any organization that’s serious about growth.
Why Viewing Innovation as a Process Changes Everything
When you think of innovation as some mysterious, unpredictable art, it feels out of your control. It suggests that game-changing ideas are just for a gifted few and that success is purely a lottery. But when you start treating innovation as a process, you turn that art into a science you can actually manage.
Think of it like a master chef creating a signature dish. The incredible meal that ends up on the plate isn't a happy accident. It’s the result of a tested recipe (the process), excellent ingredients (the ideas), and honed skills (the tools). In the same way, the most innovative companies don't just sit around waiting for inspiration to hit. They build reliable systems to find and grow it.
From Reactive to Proactive Innovation
Adopting a process-based mindset shifts your entire company from being reactive to proactive. Instead of just hoping the next big thing falls into your lap, you're actively creating the environment where great ideas are born and can thrive. This approach gives you some huge advantages:
- It becomes manageable: You can break it down into clear stages, assign people to own them, and put the right resources in the right places.
- It becomes measurable: You can actually track your progress, see where things are getting stuck, and learn just as much from your failures as your successes.
- It becomes repeatable: Once you figure out a process that works, you can use it again and again for different projects, building a reliable engine for growth.
"The ability to conceive, develop, deliver, and scale new products, services, processes, and business models for customers… is the process of taking an idea from inception to impact."
This structured way of working takes the mystery out of creativity. It makes innovation a dependable, accessible part of how you do business. You stop hoping for innovation and start building it.
The Ultimate Competitive Advantage
At the end of the day, the biggest win here is a massive competitive advantage. While your competitors are still waiting for that lightning bolt, your organization has a system for consistently generating, testing, and launching new ideas. To dig deeper, you can explore a more complete overview of the different definitions of innovation in business and see how this plays out across industries. This turns innovation from a rare, unpredictable event into one of your core business strengths, putting you in the driver's seat to lead your market instead of just reacting to it.
The Four Key Stages of the Innovation Journey
To get a handle on innovation, it helps to think of it as a journey, not a single event. While every project takes its own twists and turns, the path generally moves through four key stages. Each stage has its own distinct purpose and set of activities, guiding you from a fuzzy idea to a real-world solution.
Here’s a snapshot of a creative team right at the beginning of that journey, deep in the idea-generation phase.
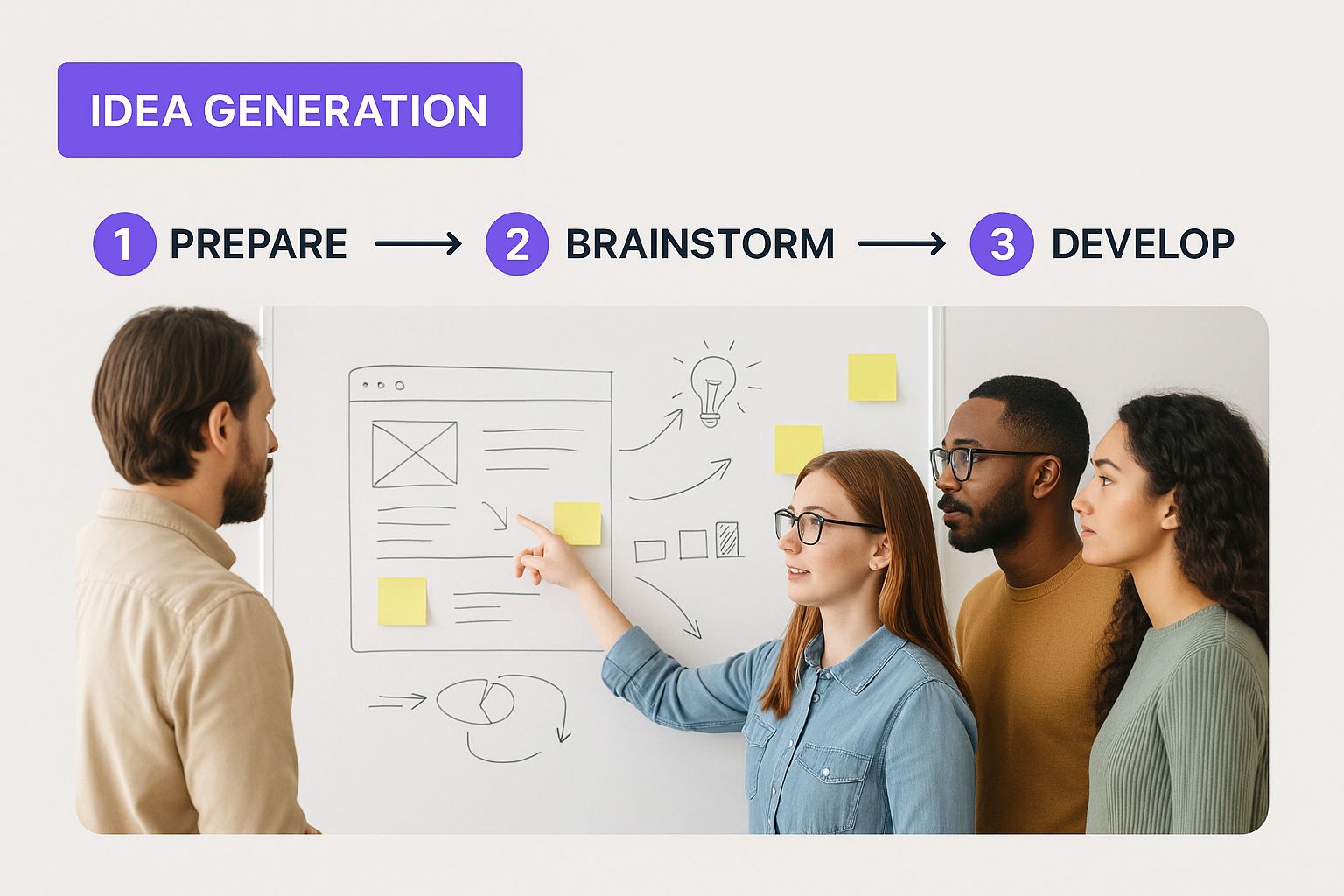
This initial exploration and creativity is where everything starts, laying the groundwork for all the hard work that comes next.
Stage 1: Ideation and Discovery
This is where it all begins—the "what if?" stage. The goal here isn't to find the perfect solution right out of the gate. Instead, it's about casting a wide net to generate a ton of ideas and spot promising opportunities.
You’ll see teams doing things like:
- Brainstorming sessions where every idea, no matter how wild, is welcome.
- Market research to uncover gaps, emerging trends, or unmet customer needs.
- User observation to see firsthand what problems people are actually struggling with.
A classic example of this in action is 3M's famous "15% Rule." It allows employees to spend up to 15% of their work time on passion projects, which has led to breakthroughs like the Post-it Note. By the end of this stage, you should have a healthy backlog of raw ideas ready to be explored further.
Stage 2: Validation and Prototyping
Okay, so you have a list of ideas. Now what? It's time to figure out which ones actually have legs. This stage is all about testing your assumptions and gathering real-world evidence before you start pouring serious money and time into a project. You're moving from "what if?" to "what works?"
The main activity here is building a prototype. This doesn't have to be fancy; it can be anything from a simple sketch or a digital wireframe to a basic physical model. Startups are masters of the "lean prototype," building just enough of a product to test the core concept with users without breaking the bank.
The mantra here is to fail fast and learn cheaply. Early feedback lets you tweak your idea—or even ditch it for a better one—before you’ve gone too far down the wrong path.
The result? A validated concept backed by user feedback and data that proves your idea is worth pursuing. For a closer look at this, you can explore the complete steps in the innovation process for more detail.
Stage 3: Development and Implementation
With a validated idea in hand, it's time to build it for real. The experimentation is mostly done, and your team can now focus on creating the full-featured product, service, or process. This is the "let's get it done" phase.
This stage is packed with detailed design, engineering, coding, or manufacturing. It requires solid project management to keep everything on schedule and tight collaboration across departments to make sure the final result is true to the original vision. The outcome is a polished, market-ready solution that's ready to go.
Stage 4: Scaling and Diffusion
The final stage is all about getting your innovation out into the world and making sure it sticks. Launching is just the beginning. Now you have to drive adoption and make your solution a part of your customers' lives or your company's workflow.
This means marketing, sales, distribution, and constantly gathering user feedback to inform future updates and improvements. Ultimately, you want your innovation to become self-sustaining and grow. It's a continuous cycle, proving once again that innovation is a process, not a one-and-done project.
Choosing Your Innovation Playbook
https://www.youtube.com/embed/A27bwuSw52I
Knowing the stages of innovation is one thing, but actually navigating them successfully is another. Think of it like knowing the rules of a game versus having a winning strategy. To turn your innovation process from a vague map into a concrete plan, you need a playbook—a proven framework that guides your team's every move.
There's no one-size-fits-all playbook. The best one for you will depend on your company's culture, your specific goals, and how much risk you're willing to take. Let's walk through three of the most popular and effective models that companies rely on to bring their ideas to life.
The Stage-Gate Model
Imagine you're building something massive and expensive, like a new car or a pharmaceutical drug. You can't afford a major misstep. That's where the Stage-Gate model shines. It's a highly structured, risk-averse approach that breaks the entire innovation journey into distinct stages.
Between each stage is a "gate"—a formal review meeting where key stakeholders decide if the project has met specific criteria to move forward. It’s a simple "go" or "no-go" decision. This rigorous process ensures that only the most promising ideas get the green light, preventing companies from pouring money into projects that are doomed to fail.
Design Thinking
While Stage-Gate is about managing risk, Design Thinking is all about people. It flips the script by starting with deep empathy for the end-user. The entire process is built around understanding their real-world problems, frustrations, and desires before you even think about a solution.
This isn't a rigid, linear path. Instead, it’s a creative and collaborative cycle with five core phases:
- Empathize: Get out there and observe, engage, and immerse yourself in your users' world.
- Define: Pinpoint the core problem you're trying to solve based on your insights.
- Ideate: Brainstorm a ton of creative solutions—no idea is too wild at this stage.
- Prototype: Create cheap, tangible versions of your best ideas to make them real.
- Test: Put your prototypes in front of actual users and gather honest feedback.
Design Thinking is perfect for creating products and services that people don't just use, but genuinely love. It ensures you're solving a problem that actually matters to someone.
The Lean Startup
In the fast-paced world of tech, speed is everything. The biggest risk isn't always losing money; it's wasting time building something nobody wants. The Lean Startup model was born to solve this exact problem. Its mantra is a continuous feedback loop: Build-Measure-Learn.
Instead of aiming for perfection, you start by creating a Minimum Viable Product (MVP). This is the most basic version of your product that can still deliver value to early customers.
The whole point is to get something into the hands of real users as quickly as humanly possible. You then measure how they interact with it and learn from their behavior. This data tells you whether to pivot to a new idea or persevere with your current one.
This approach is a lifesaver for startups or any team venturing into unknown territory. It prioritizes learning over guessing and makes sure you’re always moving in the right direction. If you need a spark to get your MVP process going, these techniques for how to generate ideas can be a huge help.
Comparing Innovation Process Models
Choosing the right playbook is a crucial first step. Each model offers a different path to success, tailored to different types of challenges and organizations.
| Model | Primary Focus | Best For | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stage-Gate | Risk Management | Large, high-cost projects in established companies (e.g., manufacturing, pharma) | Rigorous control and clear go/no-go decision points. |
| Design Thinking | Human-Centered Problems | Developing new products or services with a focus on user experience. | Creates solutions that deeply resonate with customers' needs. |
| Lean Startup | Speed and Learning | Startups and teams entering new or uncertain markets. | Minimizes wasted time by validating ideas with real-world data. |
Ultimately, the best framework is the one that aligns with your team's strengths and the nature of the problem you're trying to solve. By understanding these playbooks, you can equip your team with a clear, structured plan for turning brilliant ideas into reality.
Navigating the Bumps in the Innovation Road
Let’s be honest: even with the best framework, the road to innovation is never a smooth, straight line. It's filled with twists, turns, and unexpected roadblocks. Thinking of innovation as a process means you have to plan for those bumps. They aren’t signs you're failing; they're tests of your team's grit and commitment.
Most of the time, the biggest hurdles are people-related. You'll run into resistance from teams who are comfortable with the way things have always been done. A fear of failure can stop brilliant ideas in their tracks, as people become too afraid to take the calculated risks that lead to breakthroughs. And without a clear vision, getting leaders on board can feel like pushing a boulder uphill.
Getting through these tough spots often comes down to pure resilience. When you develop mental toughness, you and your team are better equipped to push past obstacles and stay focused when the going gets tough.
Turning Roadblocks into Stepping Stones
The secret isn’t to avoid these challenges but to have a plan for pushing right through them. It starts by building a culture of psychological safety—a space where everyone feels safe enough to pitch a wild idea or, just as importantly, to fail without pointing fingers.
When you start treating failure as a learning moment instead of a catastrophe, it loses its sting. This simple shift in mindset opens the door to the kind of experimentation that is absolutely essential for discovering what really works.
It's also crucial to get good at communicating the why behind your innovation. Don't just present an idea; sell the vision. Frame it around the company's strategic goals. Show leadership exactly how your project will solve a real customer problem, unlock a new market, or make the business more efficient. Always connect your work to the numbers they care about.
The Challenge of Measuring Real Outcomes
For so many companies, the single biggest struggle is turning a creative spark into something you can actually measure. This is where the process part of innovation really shows its value. A recent report backs this up, revealing that for 87% of innovation leaders, the number one obstacle is converting ideas into tangible outcomes. That same study found that 77% believe improving their process is the most important trigger for sparking innovation.
This tells us something vital: innovation isn't just about random strokes of genius. It’s a managed workflow that needs a structured pipeline to move ideas from a doodle on a whiteboard to a profitable reality.
To get past this, you need to look beyond immediate revenue. Tracking your progress means focusing on the right leading indicators.
- Learning Velocity: How fast are we testing our assumptions and learning from them?
- Prototype Engagement: Are real users actually interacting with our early versions?
- Idea Pipeline Health: Do we have a steady flow of new concepts coming in for validation?
By keeping an eye on these process-focused metrics, you get a much clearer picture of how you're doing. It not only helps you make smarter decisions but also gives you the hard data you need to justify more investment and keep the momentum going. You can dig into more ways to tackle these problems by exploring different creative problem-solving methods.
How AI Amplifies Each Step of the Process
Think of technology not as a replacement for a solid innovation framework, but as a powerful accelerator. Modern AI tools can supercharge each stage of your journey, acting as a tireless co-pilot that enhances, rather than replaces, human creativity. Once you see that innovation is a process, it becomes clear exactly where you can plug in AI to make that system faster, smarter, and more effective.
Instead of just brainstorming in a vacuum, AI gives your team a massive advantage. It can scan the entire global market for hidden opportunities, analyze thousands of customer reviews to pinpoint unmet needs, and even spot emerging trends before they hit the mainstream. This turns the fuzzy front end of ideation from guesswork into a data-driven discovery mission.
Supercharging Ideation and Validation
In the early stages, AI is like having a research assistant on steroids. It can synthesize staggering amounts of information, helping your team see gaps and opportunities that would have been completely invisible otherwise. This lets you generate ideas that are already grounded in real-world demand from day one.
For example, our platform Bulby uses AI-guided exercises to help teams:
- Analyze market sentiment: Find out what customers are really saying about your competitors.
- Identify adjacent opportunities: Discover new markets where your current strengths could be a game-changer.
- Overcome cognitive biases: AI can nudge teams with counterintuitive questions, breaking them out of old, stale thought patterns.
AI doesn't just help you come up with more ideas; it helps you come up with better ideas. It grounds your creative process in reality, significantly improving the odds that your concepts will resonate with actual customers.
Optimizing Development and Implementation
Once you've landed on a concept and validated it, AI's role shifts to optimizing the development workflow. It can help project managers allocate resources more effectively, flag potential bottlenecks in the production schedule before they become problems, and even automate parts of the coding or testing process. All of this dramatically shortens the time it takes to get from a validated prototype to a market-ready product.
To get a feel for how artificial intelligence is already shaking up development workflows, this guide on AI for DevOps is a great read. It shows just how these tools are making delivery cycles faster and more reliable.
Ultimately, weaving AI into the innovation process just makes every step more efficient. It frees up your team from the tedious research and logistical headaches, letting them focus on what humans do best: strategic thinking, creative problem-solving, and building truly remarkable solutions.
Building an Ecosystem for Continuous Innovation

Real, game-changing innovation almost never happens in a vacuum. Once you understand that innovation is a process, the next logical step is realizing that this process flourishes when it's part of a much bigger, interconnected system. The best ideas don't spring from a lone genius in a lab; they emerge from a dynamic mix of different people, industries, and perspectives all interacting with each other.
A great way to think about it is like a rainforest. A single tree might be impressive, but the real magic is in the complex web of relationships between all the plants, animals, and microorganisms. They all share resources and create a self-sustaining environment. In the same way, a strong innovation ecosystem connects startups, corporations, universities, and investors, creating fertile ground where new ideas can actually take root and grow.
Thinking Beyond Your Company's Walls
The old-school model of a top-secret, internal R&D department just doesn't cut it anymore. Today's leading companies know they don't have a monopoly on good ideas. Instead, they actively build networks to tap into a much wider pool of talent and knowledge.
This is exactly why we see global innovation hubs thriving. These are places that cultivate a special kind of culture where:
- Knowledge is shared openly: Universities and research centers lay the foundational groundwork that startups can then build upon.
- Talent is diverse and fluid: Experts often move between big corporations and agile startups, cross-pollinating ideas and skills along the way.
- Capital finds its way to promising ideas: Investors provide the critical fuel needed to turn bold concepts into real, functioning businesses.
The big idea here is that a healthy innovation process is an open, connected system—not a closed, internal function. When you engage with the outside world, you gain access to perspectives and capabilities far beyond anything you could develop on your own.
Innovation Is a Global Community Effort
This move toward collaborative ecosystems is happening all over the world. Just look at the World Economic Forum’s Technology Pioneers program. It’s a perfect example of how innovation has become a community-driven, multinational effort. A recent group featured 100 companies from 28 different countries, showing that breakthrough work is happening far beyond traditional hotbeds like Silicon Valley.
Creating this kind of collaborative spirit is just as crucial for teams working together from different places. Our guide on fostering innovation in remote teams offers practical tips for building that connected culture, no matter where your team is based. To really build an ecosystem for continuous innovation, it helps to look at proven methods. For instance, you can find great inspiration in various continuous improvement examples that demonstrate how small, consistent changes can lead to massive breakthroughs over time. By adopting an open mindset, you can turn your internal process into a powerful, self-renewing engine for growth.
Got Questions About the Innovation Process? Let’s Clear Things Up
Even when you understand that innovation is a process, putting it into action can feel a bit overwhelming. It's one thing to talk about theories and models, but another to actually get started. Let's tackle some of the most common questions that pop up when teams decide to move from theory to reality.
How Can a Small Team Start This Process?
Great news: you don't need a massive R&D budget. For small teams, the best way to dive in is by adopting the Lean Startup mindset. Start small. Pick one single, well-defined customer problem and brainstorm ways to solve it.
Your initial goal isn't to build the perfect, feature-packed product. Instead, focus on creating a Minimum Viable Product (MVP). This is the most basic version of your idea that still allows you to test if you're on the right track. This approach keeps your costs down and helps you learn incredibly fast from real customer feedback before you invest too much time or money.
What Is Leadership's Role in This Process?
Leadership isn't just involved; they're essential. Think of them as the primary champions for an innovative culture. Research consistently shows that one of the biggest roadblocks to new ideas is a simple fear of risk. Leaders have to actively dismantle that fear by building psychological safety.
So, what does that look like in practice? Leaders need to:
- Set the tone: Make it crystal clear that innovation isn't just a buzzword—it's a core part of the company's strategy.
- Encourage experimentation: Celebrate the smart risks, even the ones that don't pan out. Reframe failures not as mistakes, but as valuable lessons learned.
- Provide resources: Give teams the time, tools, and support they need to explore new concepts without feeling like they're being punished for stepping away from their daily to-do lists.
"A leader's most important job is to build a culture where it's safe to try new things. Without that, even the best process will stall before it ever gets started."
How Do You Measure the Success of Innovation?
This is a big one. Success isn't just about the final revenue number. If you wait until a product launch to measure anything, you've waited too long. Especially in the early stages, you need to track indicators that prove you're moving in the right direction.
Focus on metrics that track your progress and learning along the way. Consider these:
- Idea Velocity: How many new ideas are you generating and adding to your pipeline each month?
- Experimentation Rate: How many prototypes or tests is your team actively running?
- Learning Velocity: How quickly are you proving or disproving your key assumptions with real-world data?
Keeping an eye on these numbers gives you a much healthier, more realistic view of how well your innovation engine is running. It shows the process itself is working, long before you have a finished product to sell.
Ready to transform your team's creative potential into a reliable, repeatable process? Bulby provides the AI-powered guidance and structured exercises you need to supercharge your brainstorming and turn great ideas into actionable results. Start your journey at https://www.bulby.com.

